The GA4 is a highly effective analytics platform that offers useful information on how users interact with websites and mobile applications. One of its key features is the ability to track events, which are user interactions or actions you want to monitor. Understanding GA4 event parameters is crucial for gaining deeper insights into these actions and optimizing your tracking strategy. This article will explore the steps to find event parameters in GA4 and their significance.
There are different kinds of events that can be automatically collected or implemented in Google Analytics for your website or app:
Automatically collected events:
These events are collected automatically when you initially set up Google Analytics on your website or app.
Enhanced measurement events:
When you enable enhanced measurement in Google Analytics for your website or app, these events are collected along with the automatically collected events.
To view and analyze certain types of events in Analytics, you need to implement them specifically:
Recommended events:
These events have predefined names and parameters, and it is recommended that you implement them. You can access existing and future reporting capabilities in Analytics using these events.
Custom events:
These events are events that you define yourself. They should be created only when the predefined events do not suit your needs. Custom events may not appear in most standard reports, so you need to set up custom reports or explorations for meaningful analysis of these events.
Real-Time Event Collection in Analytics:
Ensuring Successful Collection of Events from Your Website or App.
Real-Time Report:
The Real-Time Report displays the number of times your website or app users have triggered each event within the last 30 minutes. You can see the specific event names and the corresponding count of triggers. In addition, you can view the parameters associated with an event by clicking on an event.
Debug View Report:
The Debug View Report allows you to see all the events a single user triggers. This report helps confirm if you have correctly set up an event and its parameters. Before using this report, you need to enable debug mode.
How Does GA4 Track Event Parameters?
In Google Analytics, you can send events with additional details called parameters. Parameters provide extra information about the event. For instance, when the “page_view” event is sent to your reports, it includes parameters like “page_location” and “page_referrer” The “page_location” parameter shows the URL of the page someone viewed, while the “page_referrer” parameter shows the URL of the previous page they visited. Here’s an example of how a “page_view” event appears in Google Analytics, along with its parameters. In addition, Google Analytics will automatically send parameters with each event. These can include:
- The ga_session_id parameter includes the unique identifier assigned by Google Analytics for the user’s session.
- The page_location parameter sends the URL of the page currently being viewed.
- The page_title parameter sends the title of the page currently being viewed.
- The page_referrer parameter sends the URL that someone viewed before the current page. This can include other pages on your website or third-party websites (if someone clicked through to your website from another website).
For events automatically tracked by Google Analytics, additional parameters are also sent.
Automatic Events in Google Analytics 4:
Once you include the Google Analytics 4 tag on your website, it will automatically monitor various events whenever someone visits a page. As an illustration, Google Analytics will automatically track an event when a person spends a minimum of 10 seconds on your website. Events tracked automatically include:
| Event Name | Description |
| Page View |
Tracked when a user visits a specific page on your website or app. |
| Screen View |
Recorded when a user navigates to a specific screen in your mobile app. |
| Event |
Captures various predefined events such as button clicks or form submissions. |
| Ecommerce |
Tracks transaction-related events, including purchases and product interactions. |
| User Timing |
Measures the time taken for specific user actions or processes. |
| Social Interaction |
Captures interactions with social media buttons or shares. |
| Exception |
Records errors or exceptions encountered during user interactions. |
| Ad Click |
Captures user clicks on advertisements displayed on your website or app. |
| Ad Conversion |
Records when a user completes a goal or conversion related to an advertisement |
Enhanced event measurement:
Enhanced measurement lets you track user interactions with your content by activating events within the Google Analytics interface. Again, no coding is necessary for this setup. Once you enable these options for a web data stream, your Google Analytics tag will immediately start sending events.
To enable or disable enhanced event measurement in Google Analytics, follow these steps:
Ensure that you are in the correct account and property. (Refer to the image below)
- Open Google Analytics and click on “Admin.”
- Click “Data Streams” in the Property column and select “Web.”
- Look for the “Enhanced measurement” section and slide the switch to the “On” position to enable all available options.
- Click “Settings” to customize individual options per your requirements if needed.
- You can also turn off specific measurement options in settings.
Here’s an example table showcasing different types of measurement events in Google Analytics 4 (GA4):
| Event Name | Description |
| Page View |
Tracked when a user visits a specific page on your website or app. |
| Scroll |
Captures when a user scrolls through a webpage or app screen. |
| Click |
Records user clicks on specific elements like buttons or links. |
| Video Start |
Triggered when a user starts playing a video on your website or app. |
| Video Complete |
Captures when a user finishes watching a video. |
| Form Submit |
Tracks when a user submits a form on your website or app. |
| Purchase |
Recorded when a user completes a purchase transaction. |
| App Open |
Tracked when a user opens your mobile app. |
| App Update |
Captures a user update your mobile app. |
| Error |
Trigger when an error occurs on your mobile app. |
Recommended events:
Adding these events to your website or mobile app allows you to measure more features and user behavior, resulting in more useful reports. However, these events are not sent automatically because they need additional information to be meaningful.
Here are some examples of recommended events in Google Analytics 4 (GA4), categorized by different aspects:
E-commerce Events:
| Event Name | Description |
| view_item |
Tracked when a user views a specific item in your online store. |
| add_to_cart |
Recorded when a user adds an item to the shopping cart. |
| remove_from_cart |
Captures when a user removes an item from the shopping cart. |
| begin_checkout |
Tracks when a user initiates the checkout process. |
| purchase |
Captures when a user completes a purchase transaction |
| refund |
Recorded when a user requests a refund for a purchase. |
| view_promotion |
Tracked when a user views a promotional offer or discount. |
| select_promotion |
Captures when a user selects a specific promotion or coupon. |
Content Engagement Events:
| Event Name | Description |
| Page_view |
Tracked when a user views a specific page on your website or app. |
| Scroll |
Captures when a user scrolls through a webpage or app screen. |
| video_start |
Recorded when a user starts playing a video on your website or app. |
| video_complete |
Tracked when a user finishes watching a video. |
| search |
Captures when a user performs a search on your website or app. |
| share |
Recorded when a user requests a refund for a purchase. |
| comment |
Tracked when a user leaves a comment on your website or app. |
| rating |
Captures when a user rates or reviews a product or content. |
Conversion and Lead Generation Events:
| Event Name | Description |
| sign_up |
Tracked when a user signs up or creates an account. |
| login |
Captures when a user logs in to their account. |
| submit_lead |
Recorded when a user submits their information for lead generation. |
| begin_checkout |
Tracked when a user initiates the checkout process. |
| add_payment_info |
Captures when a user adds payment information during checkout. |
| subscribe |
Recorded when a user subscribes to a service or newsletter. |
| complete_registration |
Tracked when a user completes the registration process. |
Custom Events in Google Analytics 4:
Custom events in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) are events that you define based on your specific tracking needs. Unlike predefined events, custom events allow you to track and measure unique interactions or actions specific to your website or app. For example, you can define custom events to capture user behavior, conversions, engagement, or any other meaningful actions relevant to your analytics goals. Make sure the name of the custom event is not a reserved name.
By defining and implementing custom events, you can gain deeper insights into user behavior, evaluate the success of specific actions or campaigns, and tailor your analytics tracking to align with your unique business requirements.
Here are some examples of custom events in GA4:
- Video_play: Tracks when a user starts playing a video on your website or app.
- Newsletter_subscribe: Captures when a user subscribes to your newsletter.
- Contact_form_submit: Recorded when a user submits a contact form on your website.
- Add_to_wishlist: Tracked when a user adds a product to their wishlist.
How to setup custom event in GA4:
Tag Manager: Using Google Tag Manager, you can create custom events by creating a new tag and configuring it to fire when a specific action or event occurs on your website or app. This lets you track custom events without modifying the website’s code directly.
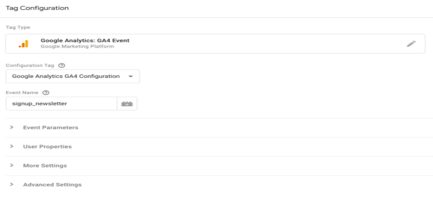
Step 1: Create a GA4 Event tag to begin
Generate a Google Analytics: GA4 Event tag specifically for the custom event you wish to track.
- In Google Tag Manager, access the Tags section by clicking on the Tags icon (depicted as an image).
- Choose the “New” option. Provide a name for the GA4 Event tag (e.g., “GA4 Event – Signup newsletter”).
- Select “Google Analytics: GA4 Event from the available options.
- Choose the appropriate Google Analytics: GA4 Configuration tag within the Configuration Tag.>
- Enter a name for the event in the Event Name field (e.g., signup_newsletter).
This will establish a new custom event; its designated name will be visible in your GA4 reports.
Step 2: Create a trigger to send the event when someone clicks the button.
Select the Triggering option within your GA4 Event tag.
- Click +on the top right.
- Enter a name for the trigger (e.g., “Trigger – Signup newsletter”).
You have the flexibility to specify the conditions for triggering the event. The event is sent based on the button label in this particular example.
- Click the Trigger Configuration box in your trigger.
- Choose All Elements./li>
- Click Some Clicks.
- Set the trigger condition: “Click Text contains Sign up for the newsletter”.
- If you don’t see Click Text, click the first drop-down and select Choose Built-In Variable. From the menu, select Click Text.
- Save all your changes.
Step 3: Before publishing your new event in Tag Manager, click Preview to see the data recorded when you click the “Sign up for the newsletter” button. When you are ready to publish your changes, click Submit.
GA4 Event Reports: Analyzing Event Data in Google Analytics 4:
To access event reports in GA4, follow these steps:
- Go to your GA4 property.
- Click on the “Reports” tab to enter the reporting section.
- Within the reporting interface, find and select the “Engagement” category.
- Look for the “Events” option and click on it to access the event reports.
In the GA4 reporting view, you can view a comprehensive list of all your logged events.
You can find out how many times each logged event was triggered.
Limitation of setting up events in GA4:
There are some limitations when working with events in Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Here are a few key limitations:
- Maximum Event Parameters:GA4 allows up to 25 event parameters per event. Each parameter can have a maximum of 100 characters for the name and 500 characters for the value.
- Maximum Event Names: GA4 supports up to 500 unique event names per property. It’s important to choose event names that are descriptive and meaningful to avoid exceeding this limit. In Google Analytics 4 (GA4), the maximum length for an event name is 40 characters.
- Data Sampling: In cases with high events, GA4 may use data sampling to process and analyze the data. This can result in aggregated or sampled data being used for reporting, which may not accurately represent the complete dataset.
- Data Retention: GA4 has a default data retention period of 14 months. This means that event data older than 14 months may be automatically deleted and no longer accessible in GA4 reports.
It’s important to be aware of these limitations when planning and implementing event tracking in GA4. Understanding these boundaries can help ensure accurate and effective data collection and analysis within the available constraints.
Conclusion:
Setting up events in Google Analytics, including GA4 migration services, is a crucial step in gaining valuable insights into user behaviour and measuring the effectiveness of your digital initiatives. Whether you opt for automatically collected events or define custom events, tracking specific interactions or actions, including GA4 migration services, provides you with a deeper understanding of how users engage with your website or app. You can monitor important metrics by setting up events, such as button clicks, form submissions, video views, social media engagement, and GA4 migration services. This data empowers you to make informed decisions, optimize your digital strategies, and improve the user experience, including GA4 migration.

We are data-driven digital marketing, data & technical consulting firm. We solve big problems with big data; deliver actionable insights & accurate foresights.