One significant transition many businesses are currently undertaking is migrating from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Google Analytics 4 is the latest version of Google’s analytics platform, providing businesses with enhanced features and benefits.
Here is the step-by-step process for seamlessly migrating from Universal Analytics to GA4.
Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with GA4 Before starting the migration process, it’s essential to understand the critical differences between Universal Analytics and GA4. GA4 is more customer-centric, focusing on events and user interactions rather than page views. In addition, it offers enhanced cross-platform tracking, machine learning-powered insights, and a privacy-centric approach. Familiarize yourself with the new terminology and concepts in GA4, such as data streams, events, and parameters, to ensure a smooth transition.
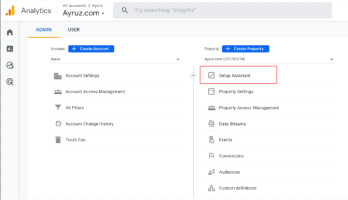
Step 2: To set up a new GA4 property to migrate to GA4, we must create a new property in the Google Analytics account; it will allow data collection in GA4 while maintaining the existing Universal Analytics property for historical data. First, open your Google Analytics account and navigate to the Admin section. Under the Property column, click on “Create Property” and select “Web” or “App” depending on the platform—the new GA4 property, including configuring data streams and defining the measurement settings.
Step 3: After setting up the GA4 property, you must update the tracking code on the website or app to send data to GA4. You can achieve this by using Google Tag Manager. The tracking code format of GA4 differs from that of Universal Analytics. Thus, it is necessary to substitute the current tracking code with the new GA4 tracking code. The process may demand alterations to the website’s code or the app’s SDK. If required, involve the development team. Ensure to thoroughly test the updated tracking code and ensure the data is collected accurately in GA4.
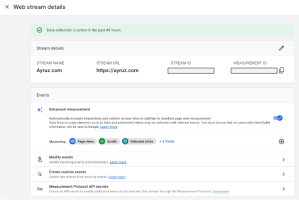
Step 4: Configure Data Streams and Events Data streams and events are the foundation of tracking data in GA4. Data streams allow us to define specific data sources or streams, such as website traffic or app usage, and events are the actions or interactions we want to track, such as page views, clicks, or conversions. Configure the data streams and events in GA4 based on the business objectives and tracking requirements. We can use the GA4 interface or the Measurement Protocol to send events directly to GA4 from the website or app.
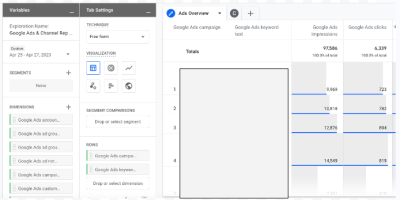
Step 5: Set Up Custom Reports and Dashboards; GA4 offers a new reporting interface with updated features and visualization options. Take advantage of setting up custom reports and dashboards that align with the specific goals and metrics. This may involve recreating or modifying the existing Universal Analytics reports suiting the GA4 reporting format. In addition, utilize GA4’s machine learning-powered insights and data visualization options to gain meaningful insights and share reports with the team and stakeholders.
Step 6: Monitor and Optimize After migrating to GA4, monitoring the data and optimizing the tracking settings is crucial. Review the data regularly to ensure that it is accurate and meets expectations. Take advantage of GA4’s advanced features, such as machine learning-powered insights and predictive modeling, to uncover new opportunities for optimization. Continuously refine the tracking strategy based on data-driven insights and make adjustments as necessary to improve the analytics performance.
List of common mistakes to avoid during the UA to GA4 migration process:
- Not planning for data loss: The data model of GA4 differs from UA, implying that GA4 will not automatically transfer all UA data. For example, GA4 may not have direct equivalents to UA’s custom dimensions, metrics, and segments and may not retain historical data entirely. It’s vital to thoroughly review the differences between UA and GA4 data models and plan for potential data loss or discrepancies during migration.
- Neglecting to update tracking code: GA4 requires a different tracking code format than UA. One common mistake is not updating the website or app tracking code to the new GA4 format, which can result in data collection issues and incomplete or inaccurate reporting in GA4. It’s vital to update the tracking code on all relevant pages or apps during migration.
- Neglects to set data retention: In GA4, you can configure data retention settings to determine how long the GA4 property will retain user-level and event-level data. If you do not set up the data retention settings correctly, the data may get automatically deleted after the default retention period of 14 months. This can lead to losing important historical data and hinder the ability to perform long-term analysis, track trends, or compare data over time. It’s important to review and set data retention settings according to the organization’s policies to ensure that valuable data is retained for the desired period and remains accessible for analysis and reporting purposes.
- Setting up where to store raw data: GA4 allows one to choose between two options for keeping the raw data: BigQuery, a cloud-based data warehouse, or the default storage in GA4. Storing raw data in the default GA4 storage, which has limitations on data access, analysis, and customization, can happen if you do not configure this setting correctly. Storing raw data in BigQuery provides more flexibility and scalability for advanced data analysis, custom data queries, and data integration with other business intelligence tools. It’s important to carefully consider and configure the storage location for raw data in GA4 to ensure that it aligns with the organization’s data strategy and enables efficient data analysis and utilization.
- Duplicate tags: GA4 allows to set up tags, which are snippets of code that collect data from the website or app and send it to GA4 for analysis. However, mistakenly duplicating tags can lead to data discrepancies and inaccurate reporting. Implementing the same tag multiple times on a page or app can send duplicate data to GA4, inflating metrics and providing incorrect insights. Additionally, duplicated tags can cause conflicts, such as multiple tags firing simultaneously, resulting in data loss or incomplete data capture. It’s essential to carefully review and manage the tags in GA4 to avoid duplications, ensure accurate data collection, and maintain reliable reporting for effective data-driven decision-making.
- Overlooking data governance and privacy considerations: GA4 includes additional data governance and privacy features, such as the ability to configure data deletion, consent settings, and data retention periods. Failing to configure these settings during the migration process properly can result in non-compliance with data protection regulations or incorrect data handling, which can have legal and reputational implications.
- Not reviewing and updating existing integrations: If you have third-party integrations with GA, such as CRM systems, advertising platforms, or other data sources, it’s important to review and update these integrations during the migration to GA4. Some integrations may require updates or modifications to work with GA4, and failing to address these changes can result in data gaps or discrepancies in the reporting.
- Not updating reporting and analysis processes: GA4 introduces new features and changes to reporting and analysis compared to UA. One common mistake is not updating internal processes and training materials for reporting and analysis to reflect these changes. Educating the team on the differences between UA and GA4 reporting and analysis and updating any documentation or training materials accordingly is essential.
- Skipping testing and validation: As with any migration, it’s crucial to thoroughly test and validate data in GA4 after the migration process to ensure accuracy and reliability. Skipping this step can result in missed data discrepancies or inaccuracies that may go unnoticed. Conduct thorough testing and validation of the GA4 data to ensure it aligns with the expectations and business requirements.
If you’re working with a GA4 agency to migrate from UA to GA4, it’s essential to communicate with them about these common mistakes to ensure they are avoided during the migration process. Collaborating with a GA4 agency can provide expert guidance and support throughout the migration process, but it’s still important to be aware of potential pitfalls. Avoiding these common mistakes and carefully planning and executing the migration process can help ensure a smooth transition from UA to GA4 and maximize the value of the analytics data in the long run. With the right approach and support from a GA4 agency, you can make the most of this powerful analytics platform and unlock new insights into your business.